Pushrod vs Overhead Cams

What makes a Mustang a Mustang? Is it the body design? That the model is Ford's longest-running nameplate? Arguably, it's the engine, especially in more modern Mustangs. In this article, we'll take a look at Ford Mustang power plants from original pushrod engines to today's overhead cam versions. Let's begin with a description of each engine type.
What Is A Pushrod Engine? What Is An Overhead Cam Engine? Dual Overhead Cam Engines The Modular V8 Story Pushrod vs Overhead Cam Mustang Engines Highlights Throughout The Mustang Years

What Is A Pushrod Engine?
Pushrod engine configurations, like those used in Mustang V8s until 1995, are relatively simple compared to today's offerings. Sometimes referred to as overhead valve (OHV) engines, pushrods use only one camshaft. Most pushrod engines use a timing chain to connect the crankshaft to the cam.
A timing chain's durability often translates into lower maintenance requirements compared to timing belt-equipped overhead cam (OHC) power plants. The cam in a pushrod is located within the engine resulting in a lower center of gravity than the cam-on-top design of OHC engines. Simultaneously, OHV engines also have more moving parts, which means that there's more potential for something to fail. This more complex configuration adds weight to the valvetrain and limits rpm capability.

What Is An Overhead Cam Engine?
On OHC engines, the single-cam (SOHC) or dual cams (DOHC) are powered by the crankshaft via a timing belt or timing chain. Every Mustang made since 1994 (the SN95 Mustang) uses a timing chain for improved durability, something that's especially important in a performance engine. Timing belts, which require periodic replacement, can fail and cause a piston to strike an open valve resulting in significant engine damage.

Dual Overhead Cam Engines
As the name implies, a dual-overhead, our double overhead, cam engine has two cams per head. Inline power plants will have two cams, and v-configuration engines have four cams. Typically, engines with four or more valves per cylinder are equipped with dual-overhead cams. An individual camshaft doesn't have enough lobes to engage all of the valves.
Engine designs with dual overhead cams can accommodate more intake and exhaust valves. A greater number of valves means an increased flow of intake and exhaust gases. This translates into a more powerful engine.

Ford's Modular V8 History
Contrary to what some Mustang enthusiasts think, the "modular" term doesn't refer to how Ford V8s are built. Instead, modular describes the engine assembly factory. In launching the 4.6L engine, Ford's first modular power plant, the company wanted an assembly operation that could rapidly re-tool as production needs to be changed to minimize factory downtime. Relying on a modular factory approach, re-tooling could be done in a matter of hours instead of days or weeks.
Despite some protests from pushrod purists, the use of modular Mustang V8s makes sense when you consider engine characteristics that are that not typical or even exist with OHV engines.
- Separate Intake and Exhaust Valves: The fundamental design of OHC engines means better air and exhaust flow and improved power.
- Variable Valve Timing (VVT): Providing individual control of intake and exhaust valves means more power and better fuel efficiency. That's music to the ears of an automaker and consumer alike. Yes, some OHV engines now offer VVT, but it can be a technological stretch.
- Higher RPMs: OHC design allows for a much broader rev range, including a higher redline that's unachievable with a pushrod engine.
- Top-End Torque: Sure, OHV engines have a low-end grunt, but overhead cam engines can quickly meet and exceed torque needs.
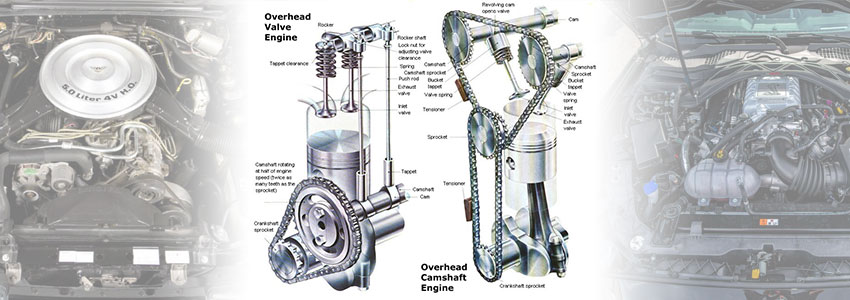
Pushrod vs Overhead Cam Mustang Engines
It's hard to argue with pushrod fans that praise engine simplicity and decades of proven, reliable performance. OHV engines are compact, provide decent power, and are easy to work on. Even high-performance Camaros still rely on pushrod engines.
As we mentioned, the basic design of OHC engines combined with the latest technology offers an efficient and powerful engine solution. It can be argued that the higher rev capability of a Mustang modular engine is better suited to handle extreme power.
The pushrod versus overhead cam engine debate will no doubt continue for some time.

Pushrod vs Overhead Cam Mustang Highlights
Ford has used more than 30 different engines in Mustangs since the model first hit the road. Let's highlight some of the standout Mustangs and their engines.

1965 Mustang: The first V8 Mustang was a pushrod design with a 260 ci displacement rated at 164 hp and 190 lb-ft of torque. The same engine, with significant modifications, was used in the same year Shelby Mustang featured an impressive 269 hp and 269 lb-ft of torque.

1970 Mustang Boss 302: The Boss 302 is about as an iconic Mustang as it gets. This 302 ci pushrod Windsor V8 featured 290 hp and 290 lb-ft of torque. The car could hit 60 mph from a standstill in six seconds flat; impressive for its day. Interestingly, there was a total of eight engine choices (all OHV) across the Mustang line-up this year.

1978 Mustang II King Cobra: While many enthusiasts would prefer to forget the second-generation Mustang II, the King Cobra was memorable perhaps for the wrong reasons, including an anemic pushrod 302 ci V8 offering 139 hp and 250 lb-ft of torque. The sluggish performance was due more to a two-barrel carburetor than output numbers. In 1972, U.S automakers switched output ratings from gross measurements to net power and torque figures. This recalculation makes earlier-year engine comparisons difficult.

1985 Mustang GT 5.0L: The first iconic modern Mustang owes its reputation to the venerable 302 ci engine reworked and rebadged with an "HO" (high output) label. Horsepower now reached 210 with torque measuring at 265 lb-ft.

1996 Mustang GT: 1996 was a breakthrough year for Mustang engines as Ford said goodbye to the pushrod 5.0 and welcomed the modular 4.6L overhead cam engine. The SOHC engine was rated for 215 hp and 285 lb-ft of torque.

1996 Mustang SVT Cobra: Seemingly eager to show off the new 4.6L power plant's capabilities, Ford reconfigured the engine design into a dual overhead configuration. The DOHC engine in the SVT Cobra offered a potent 305 hp and 300 lb-ft of torque.

2013 Shelby GT500: Not to ignore the multitude of OHC engines available in the fifth-generation (S197) Mustang, but we had to jump to the supercharged Shelby GT500 and its 5.8L V8. The DOHC engine, rated for 662 hp and 631 lb-ft of torque, and its 7,000 rpm redline clearly demonstrate that an overhead cam configure can handle hi-rev punishment.

2021 Mustang Mach 1: While perhaps not yet an iconic Mustang, the 2021 Mach 1 brings back a storied name and offers less insane performance than a Shelby-flavored Mustang. Here, OHC design provides for "only" 480 hp and 420 lb-ft of torque.
Source: Mustang Specs, Hemmings, Car Throttle





